요약
Learning
- Trying to find the pieces that fit around a random puzzle piece without knowing how each of them fit the big picture.
- If you stick around long enough, you'll find some pieces start to come together.
Binary
- Machine language/machine code - the code that computers read.
- Given to the machine and run by CPU
Process of source code -> Machine code Translation
- The two translators called the compiler and interpreter makes code readable for the computer
Translator
- Translates source language into target language
The Compiler (translator)
- Takes source text and converts it into machine code
- Souce code is turned into a file (as machine code) before even running the source code. This can be used repeatedly. ex) .exe
- uses scanner lexer/tokenizer, and parser.
- Developed by Grace Hopper, 1952. Wanted to create a new prog. language that would allow making computer programs in English. COBOL Made.
- C, C++
The Interpreter (translator)
- Takes source text and converts it into machine code, the runs/executes the code imediately. (Big difference from compiler)
- Translates sections of the code and runs it right after interpretation.
- Unlike compiler, when it wants to run the program again, it interprets this every time.
- Python, Perl
Compiler vs Interpreter
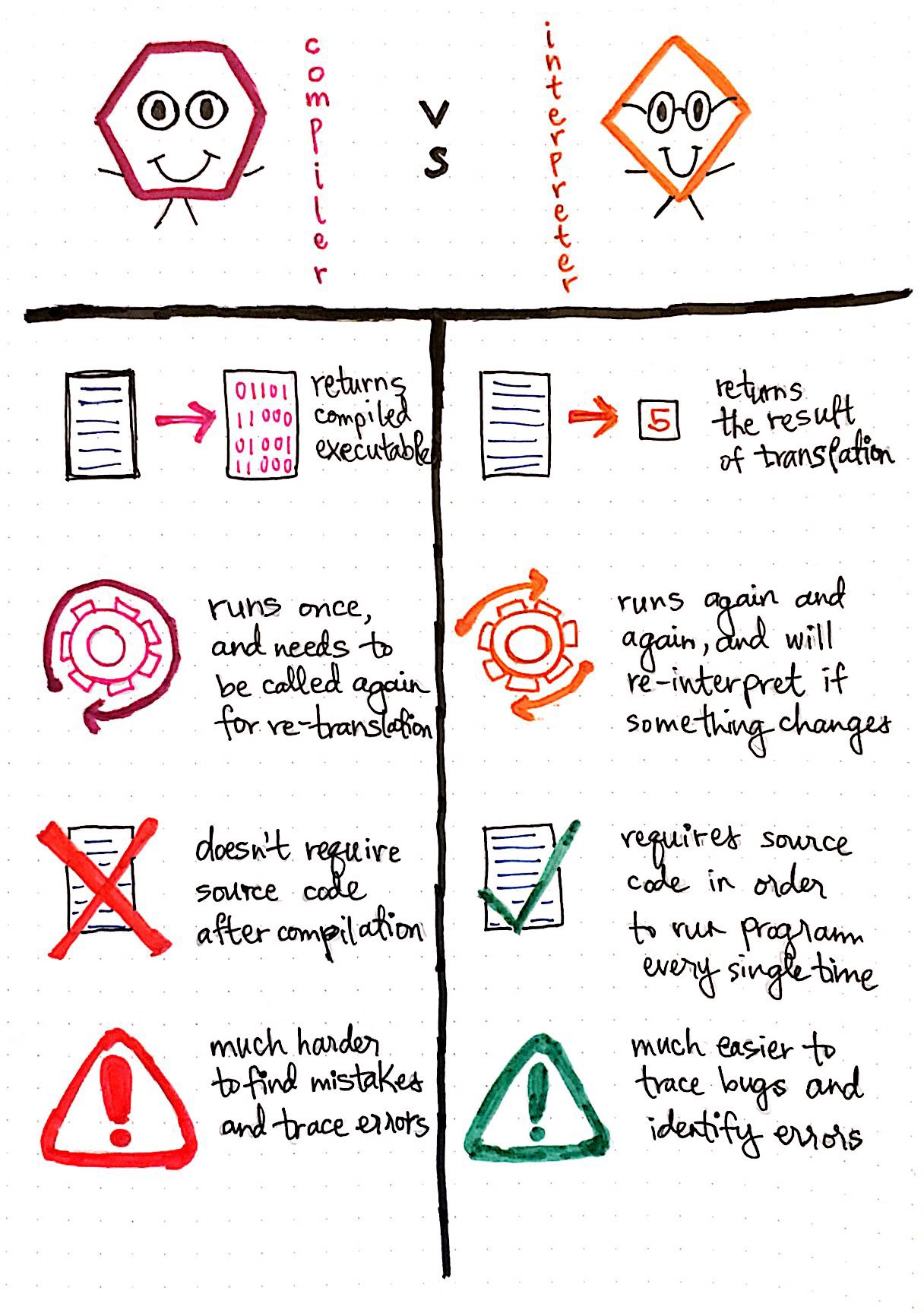
- Compiled code generally runs faster but interpreted code is more flexible (easier to test changes).
- Compiles code is distributed while protecting source code privacy but it it platform dependent.
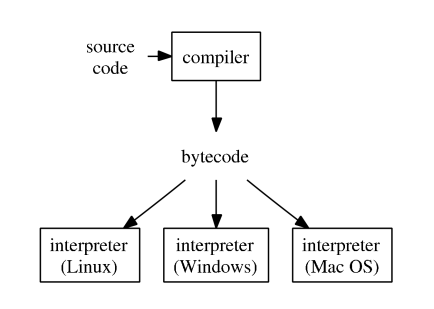
- JAVA uses both compiler and interpreter due to the usage of VM(virtual machine)
출처
https://medium.com/basecs/a-deeper-inspection-into-compilation-and-interpretation-d98952ebc842
http://www2.hawaii.edu/~takebaya/ics111/process_of_programming/process_of_programming.html
728x90
반응형